
Almost 70% of respondents do not agree with the amendment and 86% showed their concern that the amendment might give a negative impact on the investment into the Japanese equity market.

Almost 70% of respondents do not agree with the amendment and 86% showed their concern that the amendment might give a negative impact on the investment into the Japanese equity market.
My article on Japan’s unfinished reforms is online now. Lest the Abe administration and regulators “declare victory” when they are only half done, I describe seven specific measures that Japan needs to adopt in order to bring its market up to a global standard for a developed nation:
I stress the reality that in all of these, strong political leadership from the Prime Minister and other senior parliamentarians will be needed. “Thus, is it essential that the Tokyo Stock Exchange (JPX/TSE) and the various regulatory agencies keep up reform momentum. However, one senses a desire from these groups to ‘declare victory’, and they have a tendency to not fully coordinate with each other. If Prime Minister Abe’s cabinet did more to make the key players coordinate their efforts in key areas, meaningful governance change (and protection of investors) would accelerate….

When exiting minority holdings, not only beware about insider trading rules, but also short-swing profit rules. “Similar to the securities laws of other jurisdictions, Japanese securities laws also have short swing profit rules that require directors (and equivalents thereto) or 10% or greater shareholders to disgorge profits earned from matching buy-sell transactions (i.e., purchases and sales occurring within a six month window of each other, subject to certain limited exceptions) regardless of whether they are in possession of material non-public information. To avoid a costly surprise, an investor should confirm that it has not acquired any Public Company shares during the six month period leading up to the proposed share sale in order to avoid the perfunctory short swing profit disgorgement rules under Japanese securities laws. “
For companies with Softbank Group’s corporate governance structure (a company with Board of Statutory Auditors), Article 362 of Japan’s Company Law stipulates the following:
…..(4) [the] Board of directors may not delegate the decision on the execution of important operations such as the following matters to directors: [which means: “may not delegate these matters to directors or anyone else with executive responsibilities. In other words, the board must approve the following: ]
(i) The disposal of and acceptance of transfer of important assets;
(ii) Borrowing in a significant amount;
(iii) The appointment and dismissal of an important employee including managers;
etc. “”
Because of this language in the law, companies draft up “criteria for board decisions” (“fugi kijun”) , and have them approved by the board. These criteria define numerically (and in other ways if necessary) what will be considered “important” under each of the categories set forth above and therefore will require board approval, e.g. purchases of real estate larger than 1.0 Billion Yen (about $10 million), investments or acquisitions larger than 2 Billion Yen ($20 million), etc. – a “limit amount” referred to below as “X” .

In Western countries, many companies have introduced “clawback clauses” that require executives to return performance-linked compensation to the company in certain cases. In Japan, very few companies have such clauses. There are dissident voices saying things like “compensation of Japanese executives is less than in Western companies, so there is no need to do that,” or “if you want to demand the return of paid compensation, you can file a derivative lawsuit.” In this article, I would like to review the arguments that have been made so far about clawback clauses, and consider the arguments that should be made in the future.
On July 12, 2019, I gave a presentation about Work Style Reform in Japan at a seminar organized by the Japan America Society of Washington DC in the beautiful meeting room of the Groom Law Group. The talking points in my presentation were the background of the reform (political background and male dominated office), the major points of amendment to laws, the problems and keys to improving productivity, the young generation’s view of employment activity and work-life balance, protection for non-regular employees, and some implications to businesses in Japan. The questions and opinions raised by the participants were as follows.

As the person who initially proposed the Corporate Governance Code to the LDP in 2013 and 2014, I am well aware of its limitations in various areas. For this reason, I am very pleased that Fair M&A Study Group have decided that its discussions should cover not only MBOs, but also ”cases which are likewise significantly affected by the issues of conflict of interest and information asymmetry”[1], including “cases of acquisition of a controlled company by its controlling shareholder.”[2]
This indeed an important mission, because these topics include virtually all types of M&A transactions and the public statements of executives and boards with regard to them. For many years in the post-war era, the failure of the government and the JPX/TSE to set forth clear bright-line rules that facilitate a fair, robust M&A market in Japan has stunted productivity, dynamism and growth in the Japanese economy.
Mr. Ghosn’s criminal cases are ongoing. But the criminal cases alone will not put a close to this entire ordeal. It is a matter of time for Nissan to face civil cases filed by investors. Due to Mr. Ghosn’s understated compensation, it is anticipated that a considerable amount of assets will flow out of Nissan. The largest part of this outflow will be accounted for the damages claimed by and awarded to investors in civil lawsuits. What amount of assets will flow out of Nissan? This memo is an attempt to estimate the probable size of these damages.
by Nicholas Benes
This year, Japan’s governance reform drive will either keep going, or run out of steam. Judging from the amendment of the Company Law that is now underway by an advisory council of the Ministry of Justice (MOJ), the latter is likely.
Strikingly absent is a clear over-arching vision of the most important themes that amendment of the Company Law should address now that the country has a corporate governance code. In other words, what is missing, that can only be addressed via the Company Law?
If the government were truly intent on bringing about behavioral change on the part of all Japanese boards and executives, it would focus on harmonizing key aspects of the confusing array of three different corporate governance models which listed companies can adopt, and moving towards a more consistent version of the “monitoring model” for governance that has become internationally accepted and is now embodied in its own corporate governance code.
To do this, it would change the law to enable boards to flexibly appoint capable (and legally accountable) senior executives from a much wider range of candidates than is currently possible. It would also establish rules that require boards to fulfill the independent supervisory and oversight roles envisioned for them under the corporate governance code, unaffected by managerial self-interest, if they wish to delegate wider authority to executives and pay them incentive compensation determined solely by the board.
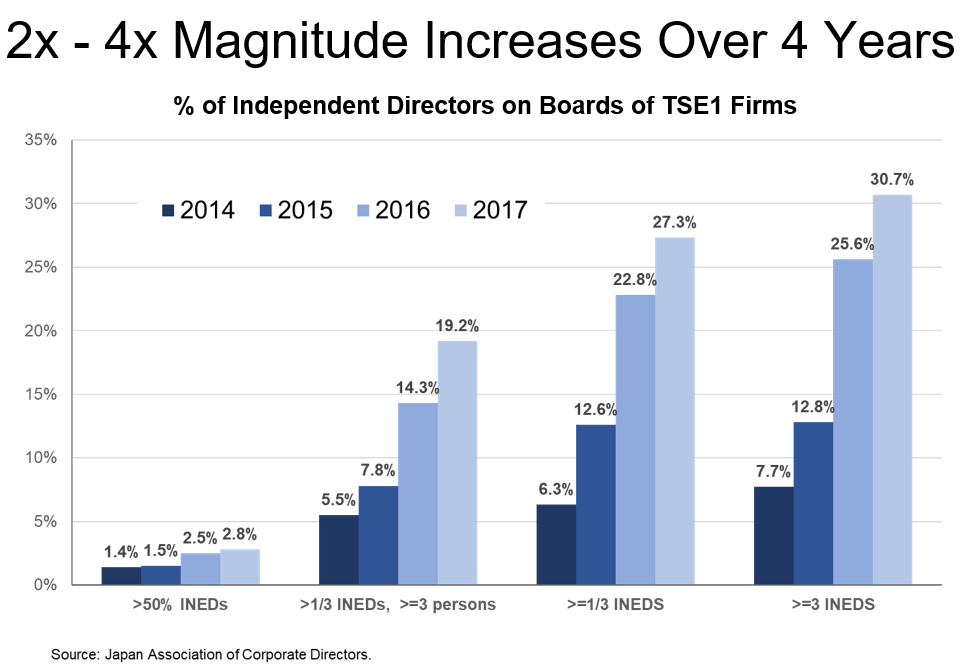
The FSA has finalized its revision of the Stewardship Code. Perhaps the biggest change is that it now encourages signatories to disclose their voting records “for each investee company on a per-agenda basis”, something I proposed to the FSA in 2010 but was ignored. However as you can see below, this is a “comply or explain rule”, thus weakening it to some extent:
“Institutional investors should disclose voting records for each investee company on an individual agenda item basis. (If there is a reason to believe it inappropriate to disclose such company-specific voting records on an individual agenda item basis due to the specific circumstances of an investor, the investor should proactively explain the reason. Institutional investors should at a minimum aggregate the voting records into each major kind of proposal, and publicly disclose them.)”