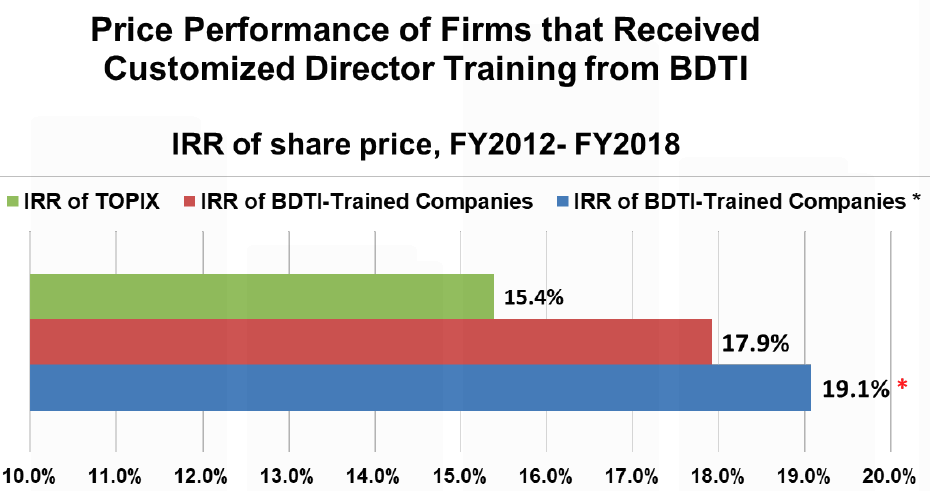
Notes: (1) On this page (at top right), you can sign up to receive our English Newsletter; (2) Sign up to receive the (separate) Japanese Newsletter here; (3) Anyone can support the “SEO” of our web site simply by mentioning BDTI on any web page with a link to this page; (4) For details about the chart, see the overview materials.
” Dear Supporter: I am writing to update you, and to respectfully ask you or your institution to make a donation of 300,000 Yen or more this year, either as a Sustaining Donor or as a Corporate Participating Member. (As explained below in section 5, the latter category now allows donors which are investing institutions to receive 40% discounts on all BDTI courses/seminars that are open to the public, and to share these discounts with companies in their portfolio.)